Body cavities and their contents
Human body Cavities
Anatomical structures are often described in terms of the cavity in which they reside. The body maintains its internal organization by means of membranes , sheaths and other structures that separates compartments. The dorsal ( posterior) cavity and the ventral ( anterior) cavity are largest body compartments. These Cavities contain and protect delicate internal organs and the ventral cavity allows for significant changes in the size and shape of the organs as they perform their functions. The lungs, heart, stomach , and intestines , for example can expand and contract without distorting other tissues or disrupting the activity of nearby organs.
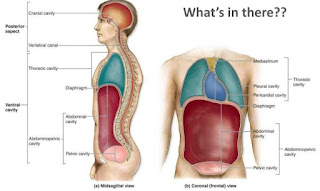
The ventral includes the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities and their subdivisions. The dorsal cavity includes the cranial and spinal cavities.
BOdy CAVITIES
1. Ventral body cavity
A. Thoracic cavity
a. Right and left pleural cavities ( Each contains a lung )
b. Pericardial cavity ( contains heart )
B. Abdominopelvic or peritoneal cavity
a. Abdominal cavity ( digestive organs)
b. Pelvic cavity ( contains urinary bladder, reproductive organs and last part of digestive tract)
2. Dorsal body cavity
a. Cranial cavity
b. Spinal cavity.
1.ventral body cavity Includes :
A. Thoracic cavity : Enclosed by the ribcage and conditions the lungs and heat .
- Pleural cavity - Each surrounds a lung : the serous membrane of each pleural cavity is the pleura.
- Pericardial cavity - surrounds the heart : the serous membrane of the pericardial cavity is the pericardium.
- Mediastinum - Central portion of thoracic cavity between the lungs: Extends from sternum to vertebral column and from 1st rib to diaphragm: contains heart, thymus, oesophagus, trachea.
B. Abdominopelvic Cavity : the diaphragm is a dome - shaped muscle that separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominopelvic Cavity. The abdomino pelvic cavity is subdivided into abdominal and pelvic cavities.
- Abdominal cavity - Contains stomach spleen liver gall bladder small intestine and most of large intestine; the serous membrane of abdominal cavity is the peritoneum.
- Pelvic Cavity - Contains urinary bladder, portions of large intestine and internal organs of reproduction. Organs inside the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities are called viscera.
2. Dorsal Body Cavity Includes :
a. Cranial cavity - Formed by cranial bones and contains brain and enclosed by the skull.
b. Spinal cavity - It is the space in vertebrae through which the spinal cord passes enclosed by the spine and contains the spinal cord.
Functions of body Cavities :
* Body Cavities protect delicate organs like brain spinal cord heard lungs etc . From accidental shock.
* They permit significant changes in the size and shape of visceral organs e.g. Many visceral organs like heart lung intestine and urinary bladder can expand and contract without distorting the activities of surrounding organs.
Other Cavities Are :
a. Oral and Digestive Cavities : the oral cavity commonly called the mouth contains teeth and tongue. The cavity is continuous as digestive cavity which open exterior at the anus .
b. Nasal cavity - Located without and posterior to the nose , It is a part of respiratory passage
C. Orbital Cavities - these are present in the skull in anterior position.
d. Middle Ear Cavities It present in skull just medial to ear drums It contains tiny bone that transmit sound vibration to inner ear.
e. Synovial Cavities : these are joint cavities which are enclosed within fibrous capsules that surround freely movable joints of the body . It secretes synovial fluid which help in lubrication and reduces friction.

Comments
Post a Comment