Body cavities and their contents
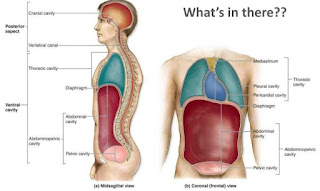
Human body Cavities Anatomical structures are often described in terms of the cavity in which they reside. The body maintains its internal organization by means of membranes , sheaths and other structures that separates compartments. The dorsal ( posterior) cavity and the ventral ( anterior) cavity are largest body compartments. These Cavities contain and protect delicate internal organs and the ventral cavity allows for significant changes in the size and shape of the organs as they perform their functions. The lungs, heart, stomach , and intestines , for example can expand and contract without distorting other tissues or disrupting the activity of nearby organs. The ventral includes the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities and their subdivisions. The dorsal cavity includes the cranial and spinal cavities. BOdy CAVITIES 1. Ventral body cavity A. Thoracic cavity a. Right and left pleural cavities ( Each contains a lung ) b. Pericardial cavity ( contains heart ) B...