Tissues including membranes and glands: types
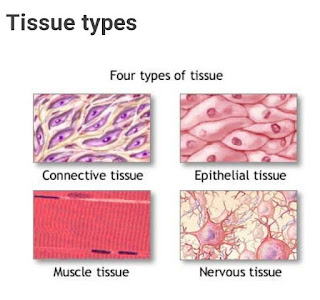
Definition A tissue is a group of cells the Usally have a common original in an embryo and function together to carry out specialized activities. Types of tissues The tissues of the consist of large numbers of cells and they are classified according to the size, shape and functions of these cells. There are four main types of tissue that each have subdivisions . They are: ¹. Epithelial tissue ². Connective tissue ³. Muscular tissue 4. Nervous tissue 1. Epithelial Tissue It covers body surface and lines hollow organs. Body cavities and ducts. It is allows the body interact with internal and y environment. Epithelial tissue consists of cells arranged in continuous sheets in single or multiple layers. Structure of Epithelial Tissue: Apical surface of an Epithelial cell faces the body surface, body cavity, lumen of an internal organ recieves cell secretion. The lateral surfaces of an Epithelial cell facing the adjacent cells on either side may contain...